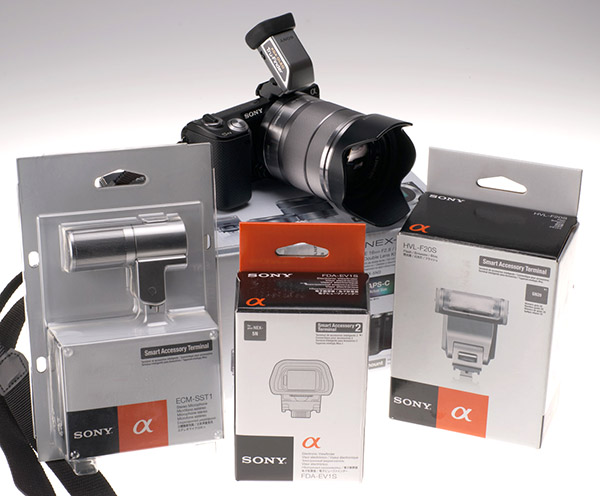
NEX-5n – sweet sixteen and expandable at a cost
Much of my NEX-7 critique was written while also using a NEX-5n outfit. I was lucky enough to find an opened NEX-5n 18-55mm kit missing its mini flash at a very low price, as new. By the time I had finished completing my NEX-5n system with bells and whistles, the total would almost have paid for a NEX-7.
The final kit consisted of the 5n, the FDA-EV1S electronic OLED viewfinder, the ECM-SST1 stereo microphone, and the HVL-F20S flash. The microphone was inherited from my NEX-5 so maybe doesn’t count. In the NEX-7 review, I start by suggesting that the 7 is really more part of the Alpha A-mount system and not the NEX system. The 7 either doesn’t need, or doesn’t accept, any of the accessories shown.
The NEX-7 finally became available after the 5n kit, and for a while both were used together. Just as the 5n can not use a plug-in stereo microphone or an Alpha system flash, the 7 can not use the NEX microphone or the HVL-F20S flash. Although I had one ‘NEX system’ with two bodies, the NEX-7 needed my HVL-F20AM flash originally bought for the Alpha 900 or one of the larger guns, and my Rode Video Pro mic, bought for the Alpha 77.
That’s why I count the NEX-7 as a hybrid, partly ‘big Alpha’ in heritage. It does not integrate with other NEX accessories, and vice-versa. Sony shows no sign of dropping the NEX Smart Accessory Terminal from 3 and 5 series bodies so this parallel range situation continues. If you’ve bought a mic or a GN 20 flash for your 5, it will not be usable with the 7 you plan to buy tomorrow.
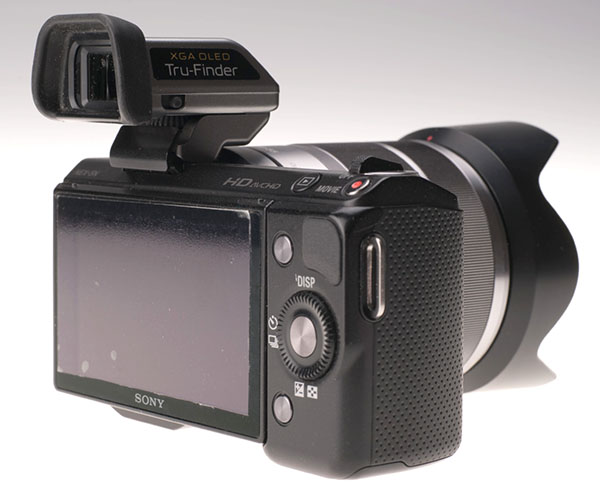
The OLED Tru-Finder
Harking back to the wonderful Minolta Dimage 7i and later the Konica Minolta Dimage A2, the FDA-EV1S slightly resembles the fragile hinged EVF of those cameras. Like them, it can be flipped into a 90° upright position or used at angles between, so the eye looks down rather like using a waist-level finder with magnifier, or a Hasselblad 45° prism.
The finder is supposedly identical to the Alpha 77 or NEX-7. It has a different dioptre adjustment, a small slider which has a huge effect for very little travel. It’s not easy to adjust but stays put when set. If you wear and remove spectacles at random, and use the camera with both the naked eye and glasses, it’s one of the least ergonomic adjustments. The eyepiece surround is a semi-hard plastic and not as comfortable or efficient as a larger soft eyecup (which Sony does not make, but would be so easy to add to the system).
The add-on finder appeared to be slightly less clear and smaller to the eye than the A77. The same goes for the NEX-7 finder. The difference seems to be in the optical train, how the lenses are arranged in the ocular itself. It may even be nothing more than an eye-surround and eyepoint issue. The OLED screen is identical but I do not seem to get precisely the same viewing experience. Maybe it’s also a little dimmer by default to conserve battery power.
In use, the way the finder sticks out behind the NEX-5n rear screen is a bonus. I’d love to get an Alpha 580, my wife Shirley uses one and she is blessed with a small nose. I’m not! The 580 eyepiece is set forward of the screen surface by a good distance. It makes a very uncomfortable viewing position for me, and add-on magnifier eyepieces don’t help all that much. The FDA-EV1S in contrast is almost perfect. The NEX-7 is better because my nose can end up beside the camera not touching it.
In practice, I ended up hardly ever using the vertical viewing position. The finder sits forward when flipped this way, and somehow my hand position wasn’t all that comfortable holding the camera and looking down at a normal scene. Instead, I found the flipped-out rear screen and a waist-level camera position more useful. Then, of course, the EVF gets in the way. The sticking out eyepiece which is so comfortably in use can obscure your view of the screen slightly.
Finally, I ended up removing the finder most of the time. It seemed a bit vulnerable, it reduced battery life greatly, it prevented pocketability with my favourite 16mm lens (or at least, felt even more vulnerable in a pocket) and much of the time I realised I was composing on the rear screen anyway. As a result the buyer of my kit got a very little-used EVF.
It is the best EVF made, or at least on a level with the best other EVFs using new technology. I can work with an EVF. Some just can’t and almost need an optical finder. But I’m not sure I would ever fork out well over £200 (or around $300 before tax in the USA) on this accessory again. I’m looking at getting a 5n back into the fold, especially after going back to my raw files. I don’t think this small accessory should cost more than a lens, and the 16mm optical finder is equally overpriced. Sony’s accessory prices generally are a negative customer experience and do not create evangelists for the system.
The vertically-angled finder was tried, but not used, for this shot with the camera near ground level. It was far more comfortable just to use the rear screen.
Enhanced vision
Somewhere out in webland, it’s been pointed out I’m old and that my opinions on EVFs (etc) may be irrelevant. That’s a bit of an own goal, as EVFs have maximum appeal to those with ageing bad eyesight. Old eyes tend to be longsighted, and can’t accommodate to close focusing, needing reading glasses as well as distance glasses in many cases. Older people find composing pictures on rear LCD screens difficult, they may have to hold the camera right at arm’s length (you see it all the time!) and even then, they may not be reading the screen menus clearly or seeing the picture at pixel-sharp quality.
It’s young eyes which work best with phones and compact cameras lacking a viewfinder. They can focus on a screen held inches away from the eye. So can older eyes with serious short sight – just remove your specs, and you are away!
The EVF, especially in the NEX-7 and as an add-on to the 5n, is a boon to these with presbyopia. Suddenly, menus can be seen sharply and pictures composed and reviewed in better detail. The dioptre slider allows correction for the most common range of near and far sight, though it can’t correct for other conditions like astigmatism. For those who must always wear specs, just removing the eyepiece ‘cup’ can help.
As with the NEX-7, one key step is to disable image review when using the finder. It is disconcerting to have the image you have just shot block your view for even 2 seconds, especially when it prevents photography. The effect is different to having the same happen on the rear screen, because while the camera is to your eye, it becomes your window on the world.
Straphanging
Here’s something not often mentioned, and once again, I end up knocking the NEX-7. The NEX-5n and previous models have simple slot-type strap connectors mounted so that the camera always hangs with the lens down, LCD screen up. Even with a 16mm only, this lens-to-the-ground position protects your lens. You can even walk around in light rain and be confident it won’t get on the glass.
The NEX-7 with its magnesium body shell uses the higher end traditional post and triangular D-ring found on the Alpha 77, Dynax 7D, Alpha 700 and 900. And it does not hang lens down like the 3 and 5 models. The strap also gets twisted more easily. No need to say which I prefer. The cheap connector may be cheap, but it has a better function.
The rear screen mounting
The mechanism of the screen on the NEX-5n is slightly better than the earlier 3 and 5, perhaps because the EVF demands it must be able to move outwards in a slightly different way to be seen clearly for waist-level shots. It is my own view that Sony missed a trick, as the EVF on this camera would certainly have allowed a reversible, fully articulated Alpha 55 type screen and its extra thickness, without impeding EVF use.
Because the rear screens of all the NEX models do not twist to allow vertical composition combined with waist or overhead viewing, it makes less difference to me whether they are hinged at all. This probably reflects the emphasis on video shooting, where vertical composition is not needed. For the still photographer, cameras with articulated screens that can orient for verticals and also aim forwards for composing self-timer groups are most desirable. The screen is there. It’s already detached from the body. All that’s lacking is the correct mechanism, even when Sony has shown they have the necessary rights or patents, and can make them.
Refinements
The NEX-5n in addition to a 16 megapixel sensor offers lens corrections (for JPEG), AF correction for Alpha lenses attached via the LA-EA2, automatic sensing of DMF (manual focus taking over from confirmed AF) with magnification and focus peaking, electronic front curtain shutter, true 50/60p HD1080 video, extended sensitivity from ISO 100 (instead of 200 minimum) to 3200 (instead of 1600 maximum), and high-speed 10fps sequence shooting (this not really matched by the focusing abilities of the camera, any more than the 1/50th second shutter lag is).
To the earlier 3 and 5 models, firmware updates have retrofitted focus peaking with or without magnification, and AF correction for lenses with the adaptor. They can’t add lens corrections, DMF, new video modes, better low light and HDR multishot modes, or change the louder double-action shutter with its 1/20th second delay.
The NEX-5n also has a touch screen. I disabled this function from the start, along with smile shutter. Face detection I leave on as this does help with focus and exposure for many shots. Since I’d parted company with my NEX-5n before using the touch screen, I can’t comment on its value. It’s just something I don’t like using.
The only advance I would argue against is the extension of Auto ISO to 3200 with no ability to control the range. Though 3200 on the NEX-5n is not unlike 1600 on the NEX-7, both these settings are too high to allow a perfectly clean image from raw after the best processing. In-camera JPEGs confirm that. I found the NEX-5n working at 3200 in many conditions where I would have been confident of a good image at 800 or even 400. This obliged me to use manually set ISO, or put up with the 3200 quality.
NEX-5n, 16mm, 1/30th at f/11, closest focus, ISO 3200, ACR conversion from raw
100% clip showing how the presence of sharp detail (wallpaper) reduces the appearance of grain compared to defocused tones (right hand side).
How good is that quality? Compared to the 24 megapixel sensor, I’d still say it’s better than a one stop advantage. One of my magazine reviews (f2 Freelance Photographer) was accompanied by a near double page spread from the NEX-5n shot above taken at ISO 3200. It’s certainly good enough for that. However, ISO 1600 is much better. ISO 1600 is so good that in decent light, you could easily be using ISO 200 off a camera of the Nikon D200 or Sony Alpha 100 era, even at 100% pixel comparison. 3200 is amazing, as you can see. But it’s definitely a grainy look where 1600 can almost be noiseless.
If a firmware update could ever achieve it, I’d like to see Sony put a maximum and minimum auto ISO selection into the NEX models, as they have done in the Alpha 77. Failing that just a maximum limit would be useful.
There is no doubt that the 16 megapixel Sony CMOS is one of the best sensors yet made, and a great balance between pixel count and image quality. See below…
16 versus 24 with ACR
Adobe Camera Raw has the ability to open files with a set of fixed size interpolations from the raw data. In this respect, it is better than Lightroom, which can export files to different sizes on demand but shows (at least from my observation) a slightly lower quality. ACR’s image sizes are slightly arbitrary and clearly are not related to the pixel dimensions of the raw image. You can open a 17.5 megapixel or 25 megapixel image from a 12, 14, 16, 18 or 21 megapixel raw.
When you select an enlarged or reduced conversion, the large image preview and editing window reflects this. Your 100% view changes to be a 100% view of the size you are producing. In the case of the NEX-7, the 24 megapixel image size is the largest option on the list. You can not open to 25 megapixels as you can with the NEX-5n. You can reduce to 17.5, 11.2, 6.3, 2.8 or 1.6 megapixels.
The largest size is always 6144 pixels wide (longest dimension), or the native size of the raw file. So a Nikon D800 image which is 7360 pixels wide also shows up with only smaller options, and rather oddly skips the 6144 24 megapixel choice. With ACR, you can not open or preview a D800 raw at 24 megapixels, only at full size, 17.5 megapixels and the smaller choice.
If the raw file has unusual dimensions – 4:3 or square for example – you may get interesting options. The 21.3 megapixel Dalsa medium format backs show a 6144-wide 28 megapixel maximum size output option. The 16 megapixel Kodak MF backs allow 5120 square or 6144 square output, the largest size being 37.7 megapixels. As these backs have no AA filter and are teamed up with unrivalled lenses, a 16 megapixel Hasselblad 80mm Planar shot scaled up to 28 megapixels is hard to tell from a native Nikon D800+zoom lens image. D800E with top grade prime beats either.
Using the NEX-5n (or the earlier 14 megapixel 3 and 5 models) ACR offers 17.5 and 25 megapixel conversion, viewing and export or opening as well as the native size and the smaller ones mentioned above. It is largely my experience using the resizing functions along with NR and sharpening that makes me prefer the 16 megapixel sensor to the 24.
This view was taken with the NEX-5n and 18-55mm at 55mm, ISO 100, happen to end at f/11 though is was intended to be at f/10 (the non-lockable controls of the NEX-5n did this to me far too often).
This view was taken a few seconds later using the NEX-7 with a different (black) 18-55mm at f/10, all other parameters being similar, and both as raw files.
Here are 100% clip sections of both images. The 5n is top, the 7 is bottom. Both files are 6000 x 4000, the 5n image was exported by Adobe Camera Raw to 6144 pixels wide. Both images use Sharpen 25, Radius 0.5, Detail 50 and zero for both luminance and colour NR. In the very subtle low contrast texture of the lamp-post and the definition of the hex nut, the 7 clearly wins but it’s a surprisingly fine margin.
Yes, the difference is obvious. The 7 wins. Think again – for this clip, I’ve put the NEX-7 native size image TOP and the NEX-5n interpolated 24 megapixel output BOTTOM. What is the conclusion? That the lens you use – even the individual sample of the lens used as no two 18-55mms will perform identically – has far more effect on usable image detail than 24 megapixels versus 16.
Scaling images down in size
When I have been editing NEX-7 images at their native 24 megapixels the NEX-5n upscaled image has sometimes looked better overall, and the native size NEX-5n image nearly always wins. The NEX-7 image misses the mark for me maybe 30% of the time. For all ISO settings above 400, I tend to set the ACR output to 11.2 megapixels. Setting it to 17.5 doesn’t lose the granular feel. ACR’s 2012 process (CS6) has noise reduction and sharpening controls which work faster and better than any of the plugins or other raw conversion programs I’ve used.
Checking as I write: for 66 images just processed from the NEX-7, Alpha 77 and Alpha 580 (16 megapixels) I counted that 33 of the 24 megapixel images had been downsized to 3600 x 2400 pixels or thereabouts to resolve issues with noise or sharpness. Not one of the Alpha 580 images had needed downsizing. The 6000 x 4000 shots could, perhaps, have been downsized to the 4912 x 3264 of the 16 megapixel sensor or the 4076 x 2731 offered by ACR; the 3600 x 2400 size is the minimum for image library Alamy. If you send them anything except the sharpest and most noise-free images, you risk having all your work rejected, your submissions placed in a slow queue, or your entire account deleted for repeatedly less than perfect technical standards.
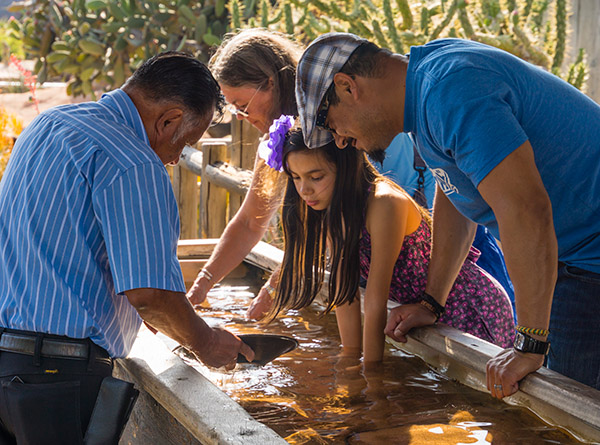
For stock library use, this image was reduced from 24 megapixels to a slightly cropped version just over 9 megapixels. The 18-200mm Tamron lens at 66mm, with the NEX-7, was used at f/8 and the focus was on the gold pan. A 24 megapixels, the degree of softening on the young girl’s face is beyond the acceptable limit; scaled down, it looks natural when viewed at 100%. Shooting with 16 megapixels instead of 24 will give an impression of greater sharpness, or greater depth of field, when checked at 100% though this is an illusion and two prints made at the same size will show no difference.
Working with the 16 megapixel sensor, across the usual range of conditions from daylight to night scenes, hardly any images need reducing in size to hit Alamy’s QC mark. Working with the 24 megapixel sensor, every image has to go through ‘is this really OK at full size?’.
While I definitely want my 24 megapixel Alphas for studio, tripod, architectural, landscape, artwork copying and similar tasks, having sold both the NEX-5n outfit and the NEX-7 if I was to purchase again it would be a NEX-5n with reservations.
Reservations
After using the NEX-7 interface, especially with the settings lock function, it is very difficult to go back to using the 5n or earlier interface. On all NEX cameras the menus are very easy to navigate, consistent, and reasonably fast. But on all NEX cameras except the 7, the rear controller is much too prone to accidental operation. The vertical straphanging reduces this a bit, as it avoids the control touching your clothing. The action is so light that just brushing against a coat or the fabric inside a camera pouch can be enough to change the aperture in A-Mode, the shutter in S-Mode, or the EV exposure correction (requires a light pressure to the bottom of the control followed by rotation).
It would be good if Sony could make a firmware modification which locked the primary function of rear controller rotation – something like a two-second press on a specified button – while leaving the compass-point click/rotate functions (located North, East, South, West or 12, 3, 6 and 9 o-clock on the controller) available.
The final reservation is where I started, about the Smart Accessory Terminal and how it differentiates the 3 and 5 models from the 7. The 7 fits well into any existing Alpha setup, the lesser models are only a partial match. The terminal has appeal. It’s long been thought that Sony could use it to add other functions, such as a GPS module or a wireless flash commander. No such accessories have appeared yet. Does that mean it’s a dead end, to be replaced by 7-style interfacing – or is the 7 a level on its own?
Sony has provided some kind of road map for lenses and would perhaps be giving too much away if they issued a roadmap for NEX development. It would make planning today’s purchases less of a gamble for existing system owners and new adopters if they could.
– David Kilpatrick
To see NEX-5n specs and prices at B&H follow this link. Clicking on our Amazon or B&H search boxes can benefit this site (many thanks to the person who keeps ordering dozens of academic books from Amazon!).