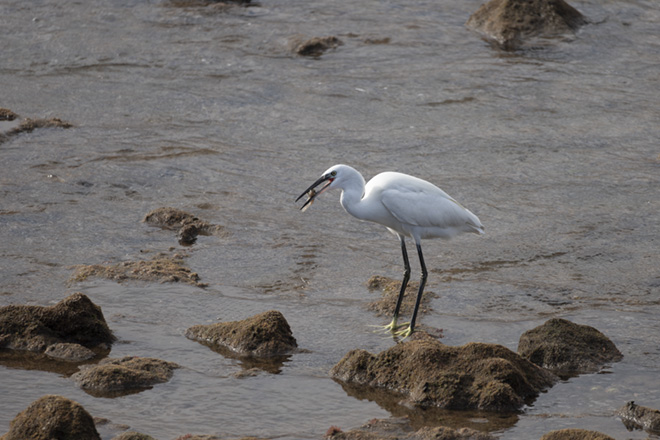
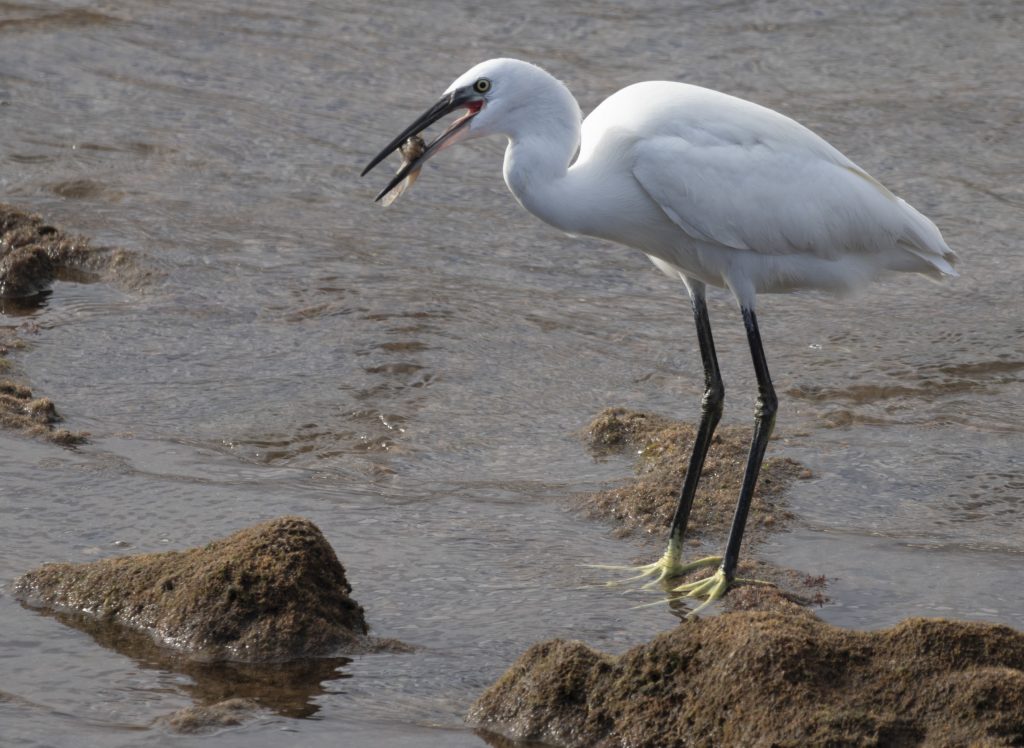
Sony E 70-350mm f/4.5-6.3 G OSS
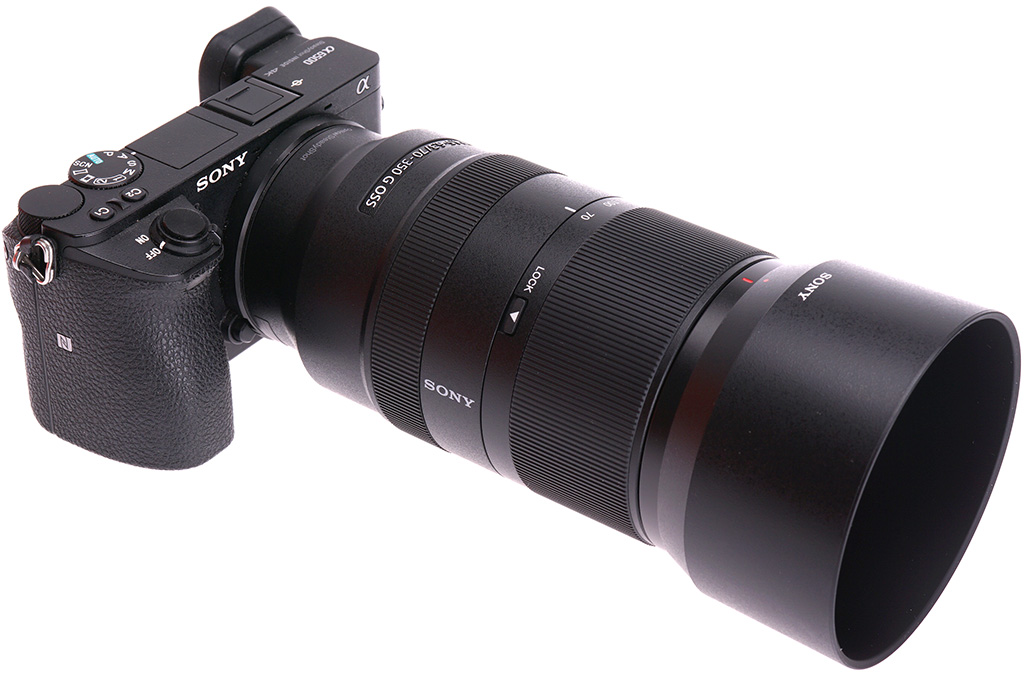

The neatest solution for sharp long tele shots on Sony A6000 series APS-C
- Excellent full aperture performance from 70 to 350mm
- OSS stabilisation works with every Sony Alpha E-mount APS-C body
- Perfect for movies with A6000, A6300, A6400 without sensor stabilisation
- Compatible with all NEX and Alpha E-mount models from 2010 on
- Enhanced OSS with A6500, A6600
- Compact and light weight
- G series optical quality, Custom Button on lens, AF/MF and OSS switches on lens
- Lens lock at 70mm to prevent zoom creep
- Single extending zoom barrel
- 67mm non-rotating filter thread
- Bayonet lens hood included
- Moisture and dirt resistant multicoating
- Coverage allows use on full frame bodies with larger than APS-C crop
This lens was purchased in October 2019 and the review is based on nine months of use on Sony A6500 (ILCE-6500), A6300 (ILCE-6300), A6000 (ILCE-6000) and A7R MkIII (ILCE-7M3). Review by David Kilpatrick.
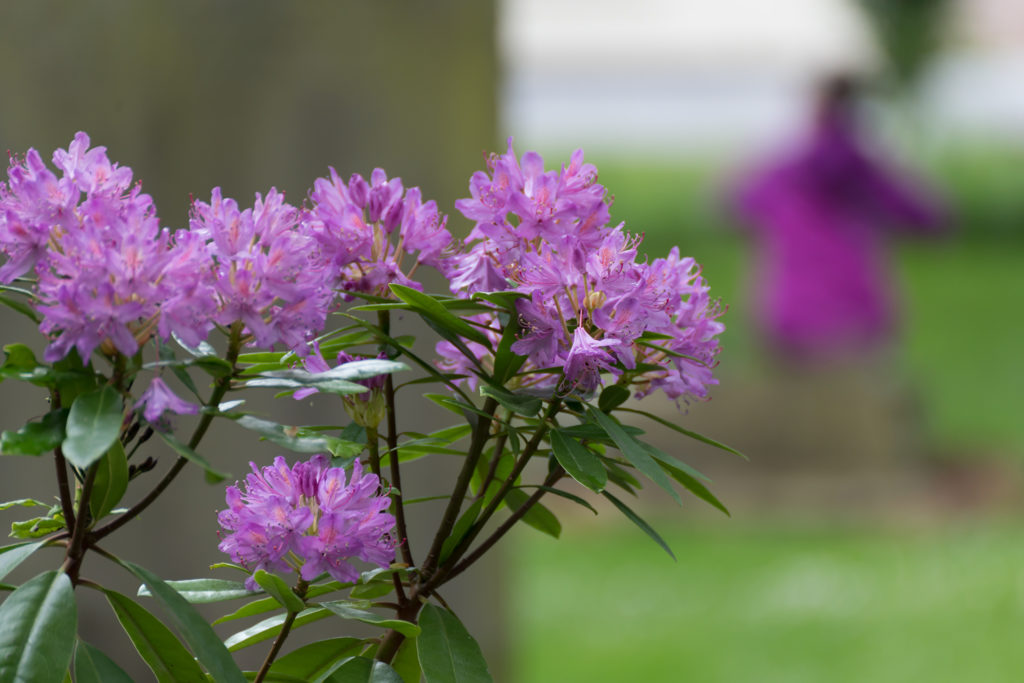
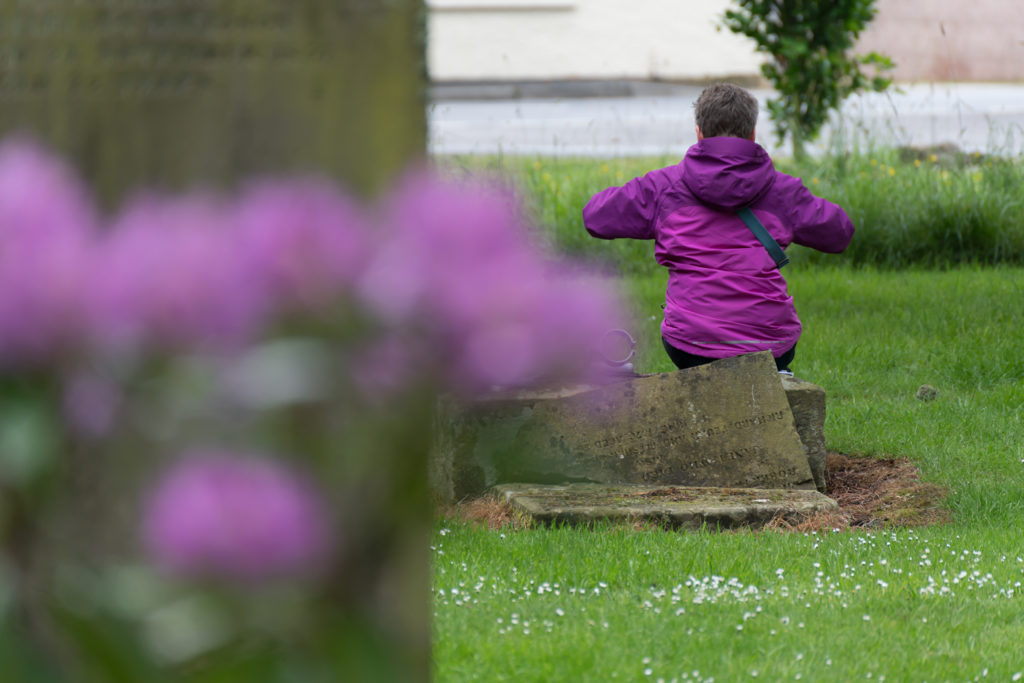
A solution for practical photography out and about – worldwide
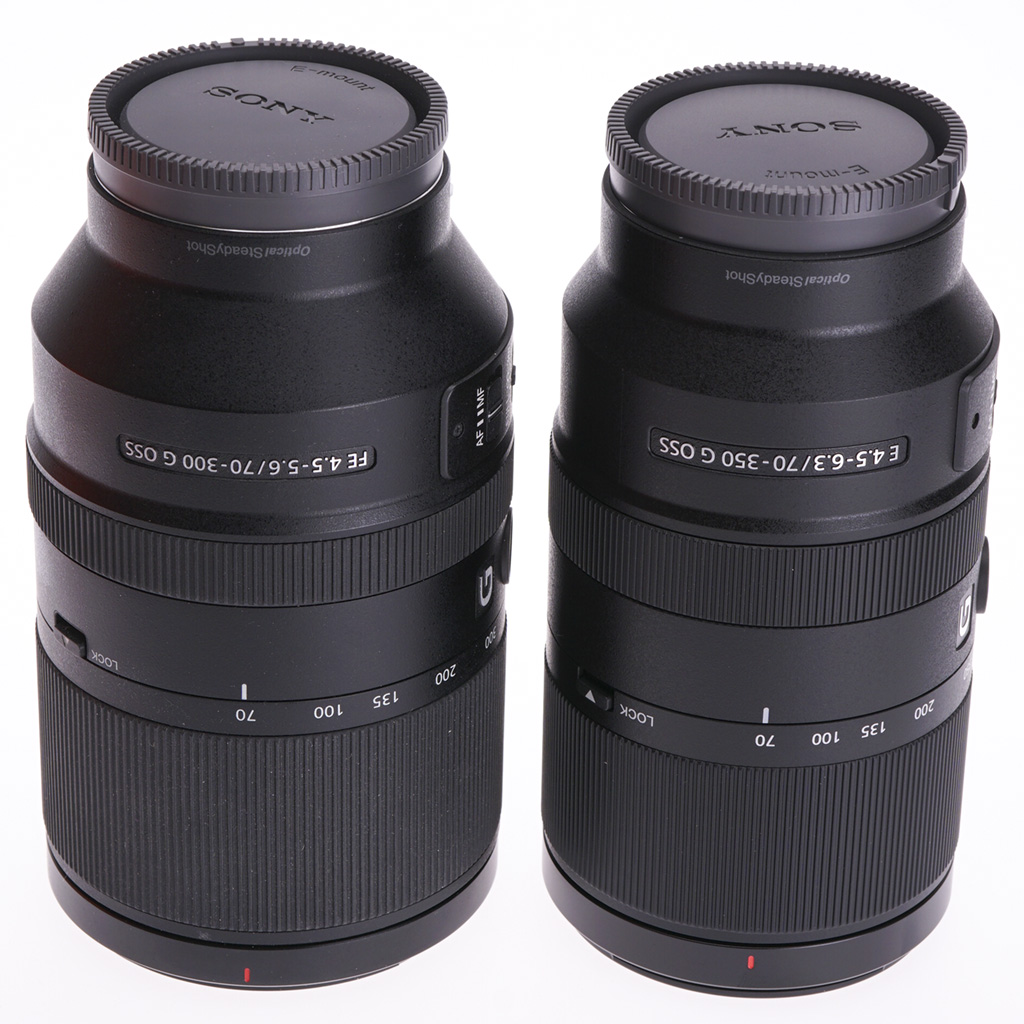

I had been using the Sony FE 70-300mm f/4.5-5.6 G OSS full frame tele zoom on my A7RIII for over a year. This lens is very sharp wide open and benefits from the best close focusing in its class at 90cm meaning a scale of 0.31X at 300mm. It weighs 854g and has a double tube zoom extension. As you can see above this lens (left) is only a few mm longer physically than the APS-C 70-350mm (right) but the extra barrel heft, 72mm filters and much larger lens hood meant it needed a bigger kit bag, and proved harder to change quickly when swapping lenses.
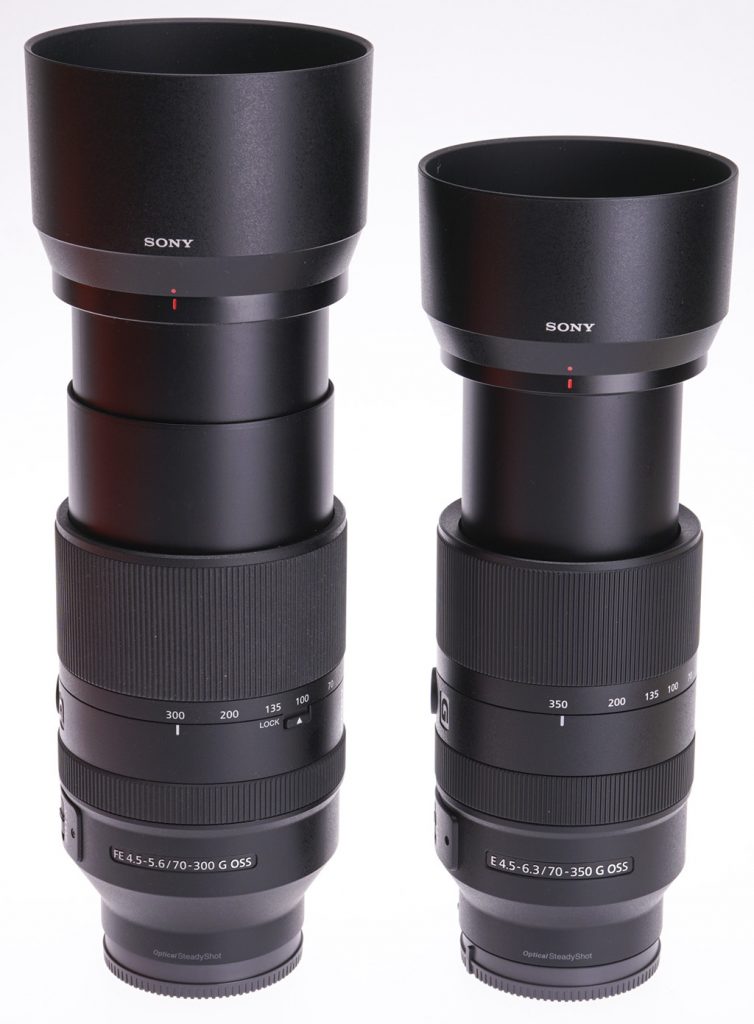

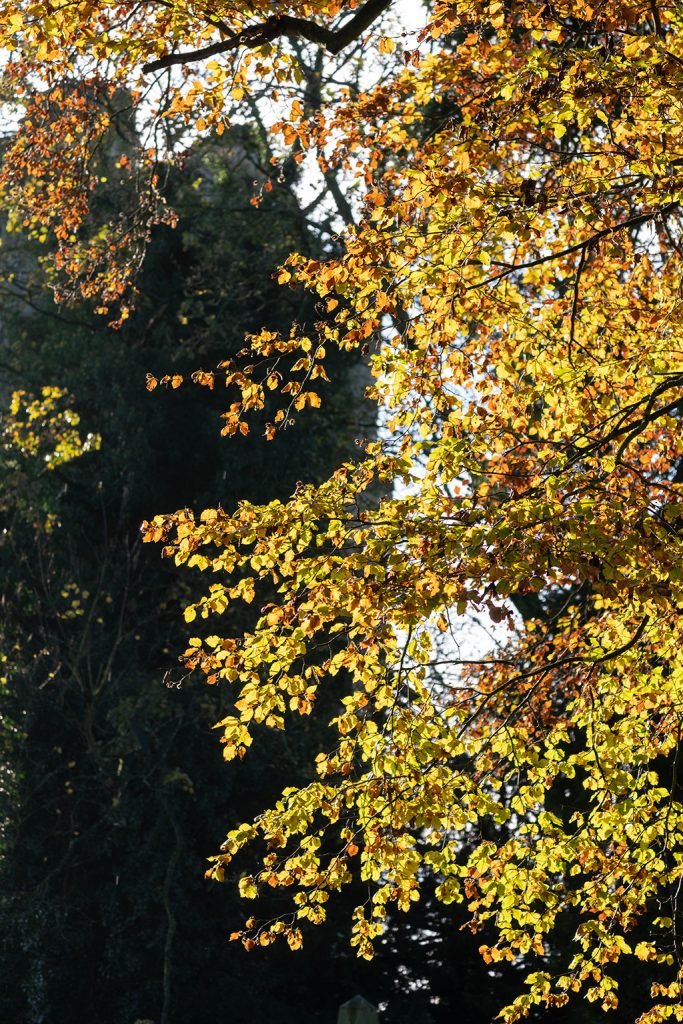
The 70-350mm for the smaller image sensor proved if anything even sharper, right to 350mm. Lenses like this often prove soft at maximum focal length and maximum aperture. The 70-300mm at f/5.6 is a third of a stop faster, but to get it as crisp as its newer little brother, it needs to be set f/6.3 – a match in speed. You can see above how much bigger the full frame lens becomes at 300mm. The 70-350mm only weighs 625g but its very fast and silent XD Linear Motor AF can only get as close as 1.5m at 350mm, 1.1m at 70mm. The maximum subject scale is 0.25X.
I knew the 70-350mm would be my choice for travel and daily use with my A6500, but I was going to miss that closer focus. The full frame lens has an AF range limiter, full range or 3m to infinity but oddly no 0.9m to 3m choice. The APS-C lens has no limiter but I have never missed it and rarely used it on the 70-300mm.
My big question was – can I do without the 70-300mm and use the 70-350mm on my full frame bodies?
Cropping power, sensor resolution and coverage
Tests quickly proved that distortion and vignetting kick in fast beyond the crop format field of view, but sharpness remains good and depending on focal and aperture you get much more than APS-C. You can almost get a full frame at close range.
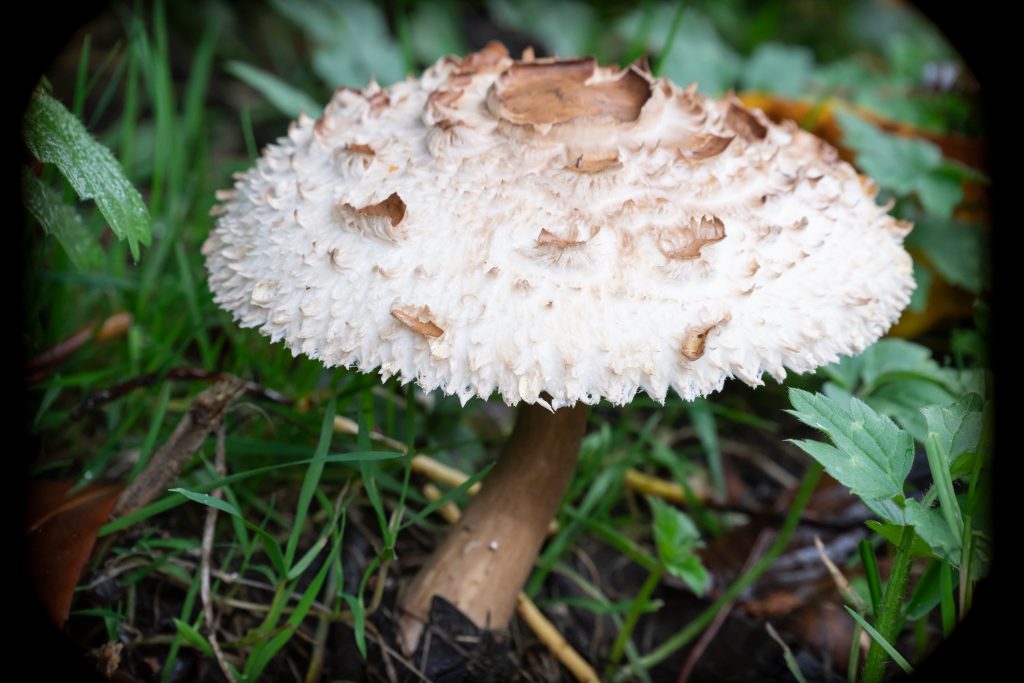

This mushroom (about hand sized) is at 350mm and f/11 on the A7RIII, and you can see the mechanical vignetting cut-off left and right. It’s caused by the lens rear baffle not the optical design – the lens could be modified to remove this, but it’s not advised.

At 70mm on a very demanding subject the distortion without lens profile, on full frame, is extreme (left) but with Lens Profile correction applied at 200% plus -8 Manual, and similar vignetting adjustment, Adobe Camera Raw or Lightroom can almost handle it. On a neutral subject like a portrait with a foliage background the coverage would be fine. More to the point, manual crops much larger than the 16 x 24mm you could expect from an APS-C lens are fully usable.
But why use a full frame body? Unless you own a Sony A7RIV (61 megapixels) you won’t actually get a more detailed distant animal or bird. The modest 24 megapixels of all the current APS-C bodies beats the 18 megapixel crop format of the A7RII/III. Canon users have much the same position, their smaller APS-C (1.6X not 1.5X) and 28 megapixel resolution matches 60 megapixels on 24 x 36mm. The advantage of full frame is that you may catch more of your subject, your framing and tracking active subjects enjoy more leeway. If your subject stays in position the smaller sensor can capture finer detail – and this is where the 70-350mm excels.
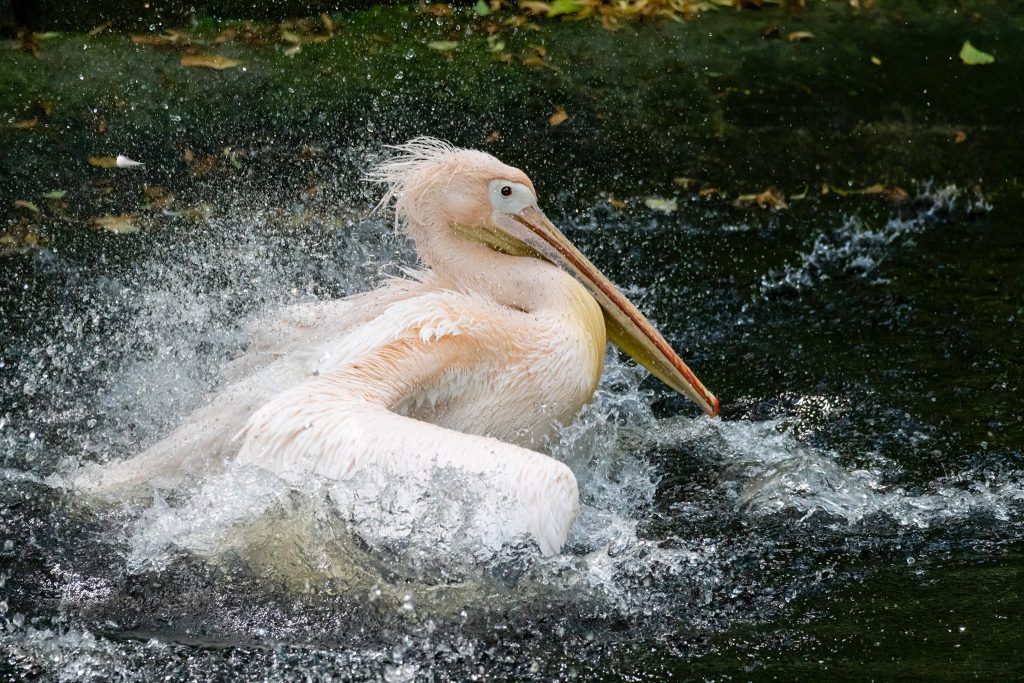

This is a good example. At 198mm on the 70-350mm on A6500, it’s the same composition I would have had with the A7RIII and 70-300mm at 300mm and that would have produced a larger more detailed image. There’s only a real benefit to the 70-350mm on APS-C when you’re near the 350mm end. Did I keep both? No – I already knew I wanted a much faster but still compact zoom for the full frame kit, and the Tamron 70-180mm f/2.8 was coming in six months’ time. So I sold the 70-300mm and decided to use the A6500 with 70-350mm for all longer tele shooting.
From the start it proved a very capable combination.
Fast lenses are not as important now
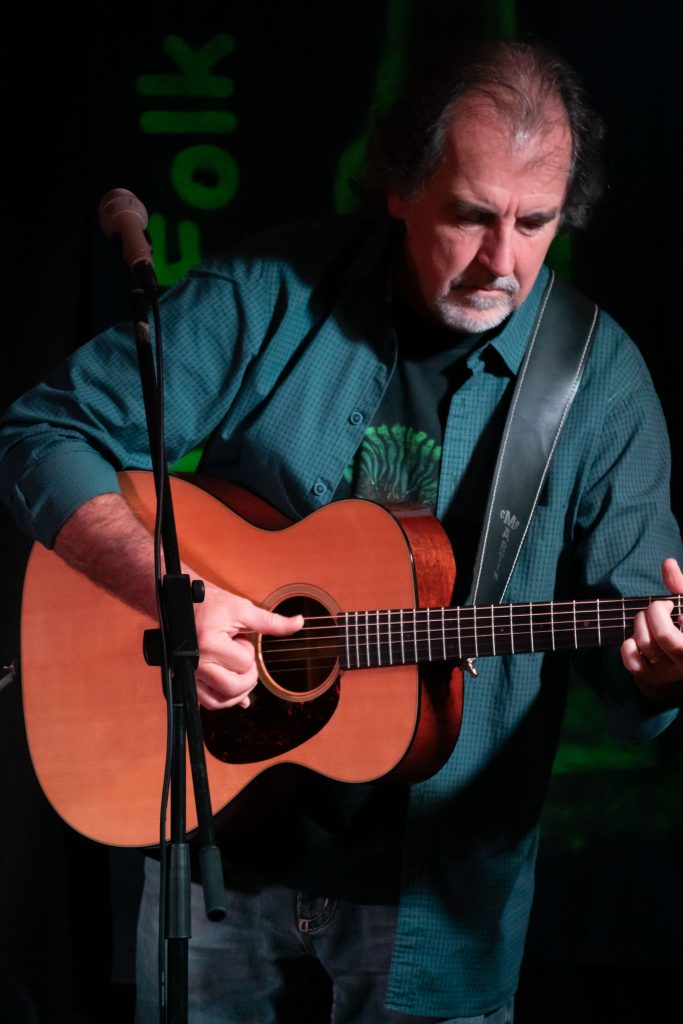
Mirrorless cameras with phase detection autofocus, good high iSO performance and better resolution electronic viewfinders have made wide aperture lenses less essential for low light. The linear motor focus of the 70-350mm rarely misses a shot regardless of conditions. One of my first shoots was a music festival, where this lens allowed me to work from the very back of the hall and never get in the way of the audience.
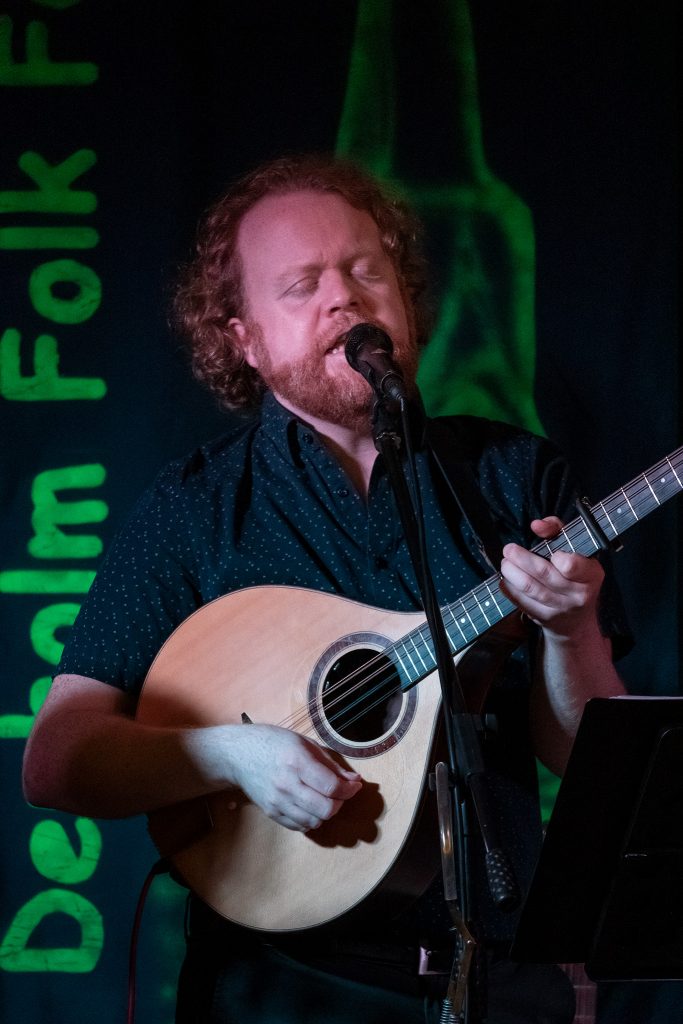

Processed from a raw file at ISO 6400, this shot of Steve Byrne performing was taken at 350mm wide open at f/6.3. The same on full frame would need a 525mm lens at f/8 and ISO 8000 (a direction Canon is taking with their new 800mm f/11 IS STM for the R mount – the working aperture no longer matters much if the viewfinder stays bright, AF is accurate and there’s not much noise at high ISO settings).
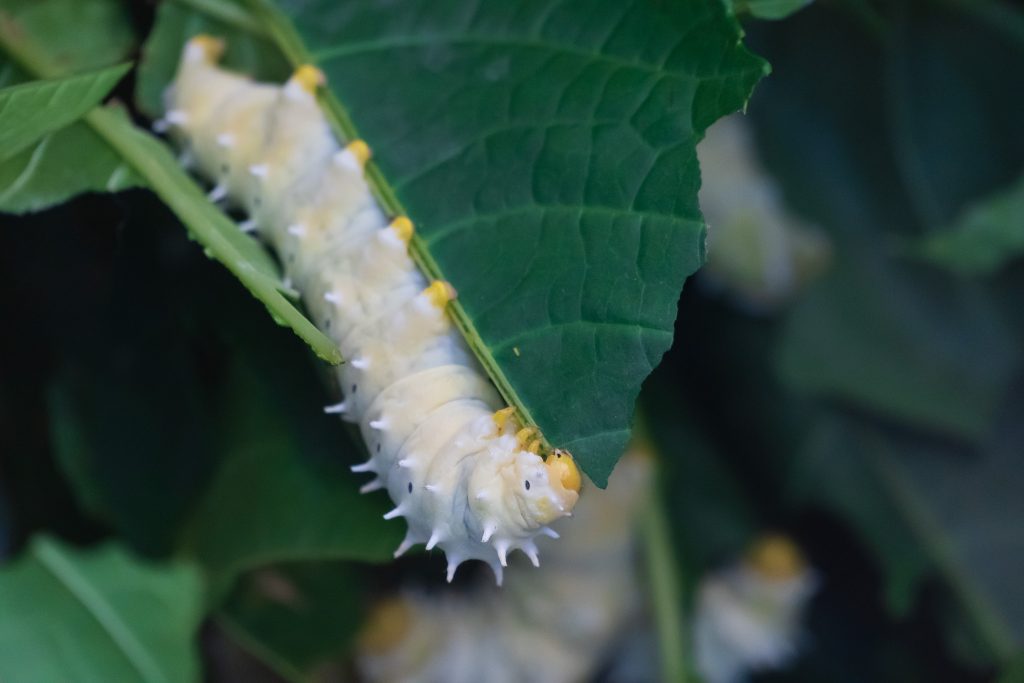

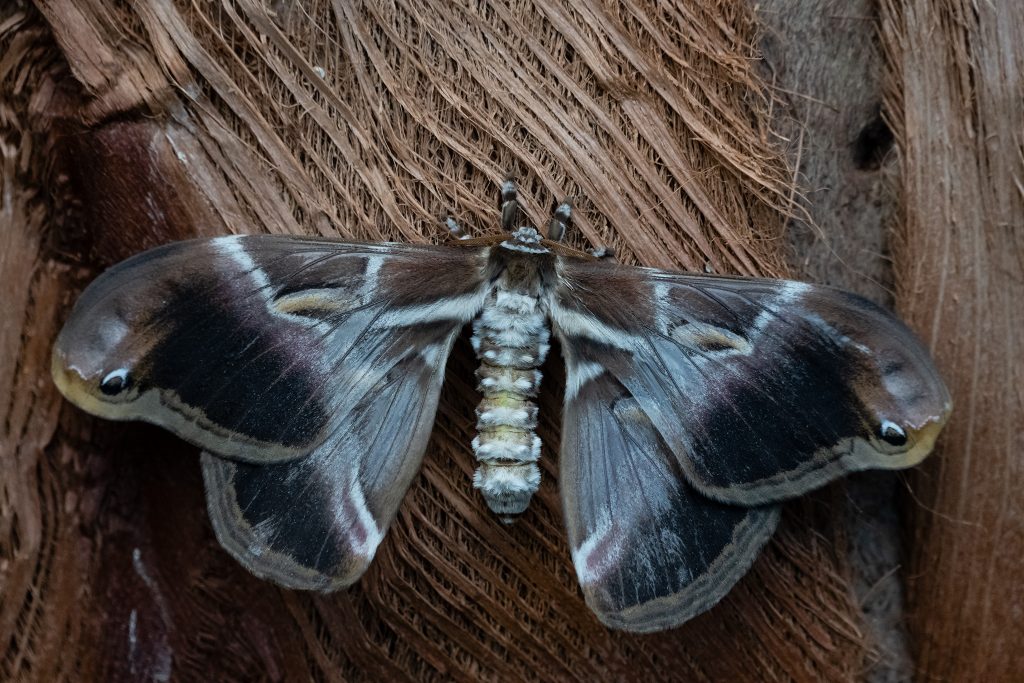
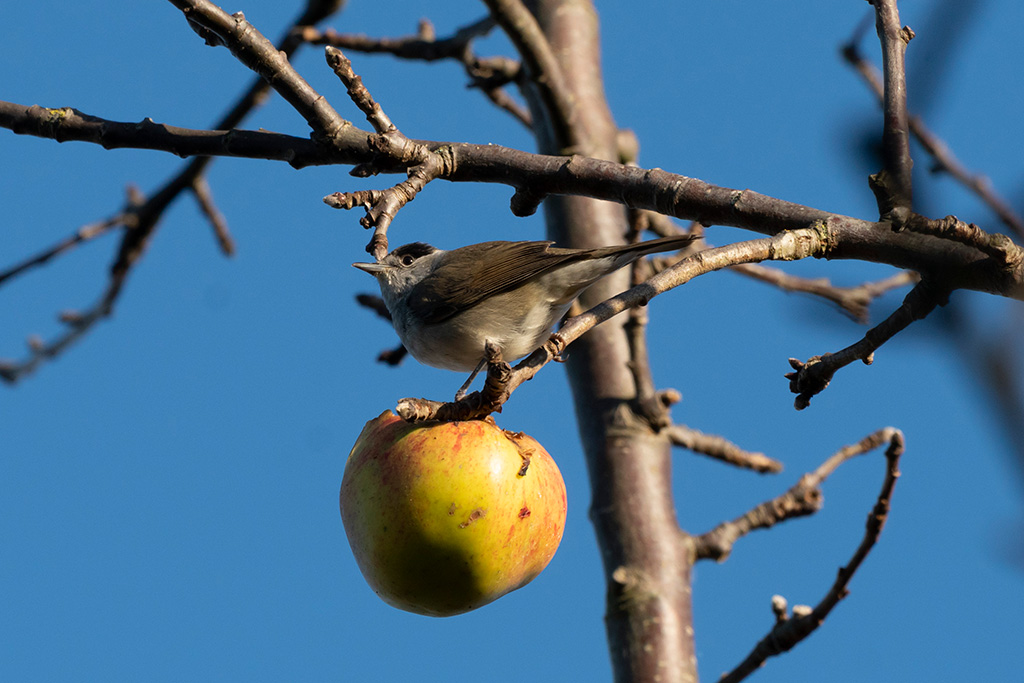
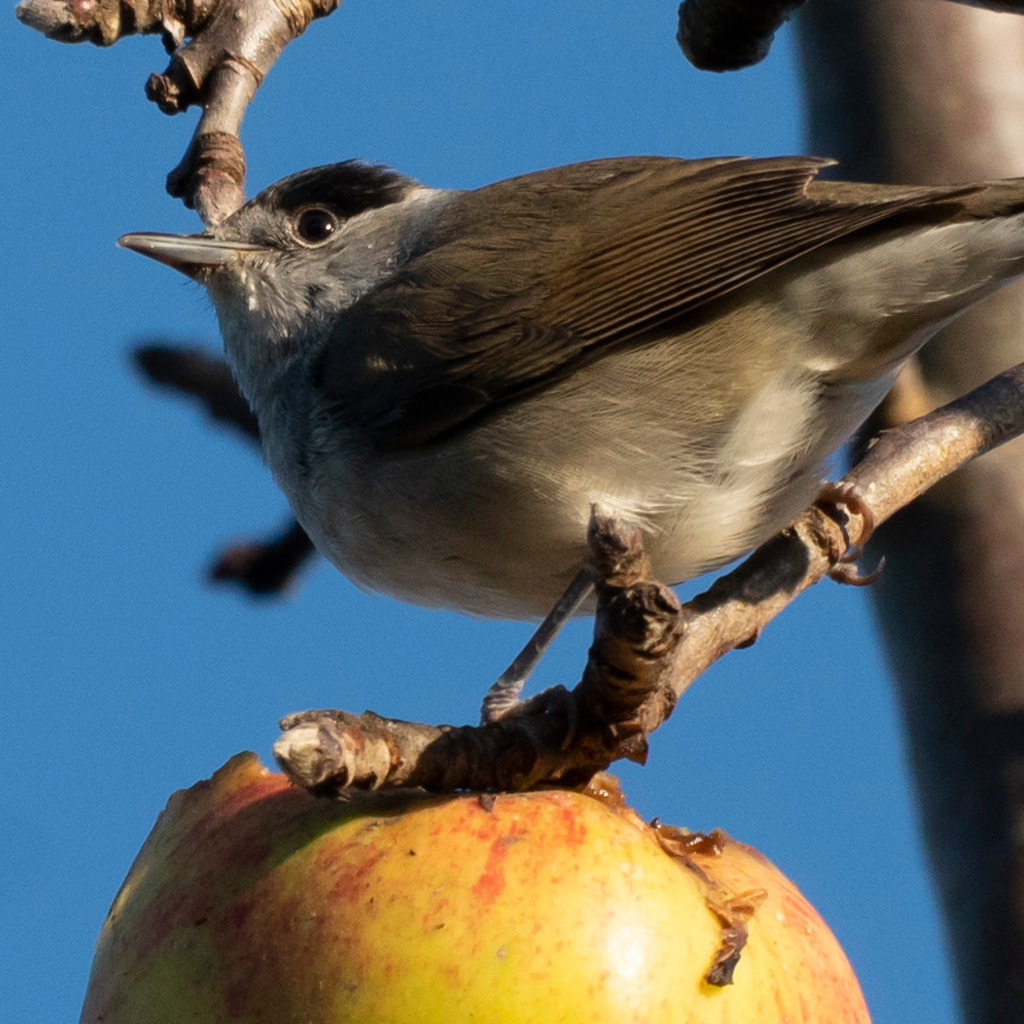
The long reach in a concert hall is one side of using a 350mm on APS-C. Here’s another – the lens may only achieve a quarter life size and need you to be 1.5m away at 350mm, but 0.25X on a 1.5X factor sensor is 0.375X in ‘old macro’ terms. Not only that, the ISO 2500 used here is about the same in grain or noise terms as an ISO 400 film and the stabilisation of this lens on the A6500 is as good as you get. A 1/125s shutter speed did not prevent tiny hairs on the caterpillar’s head being sharply resolved.
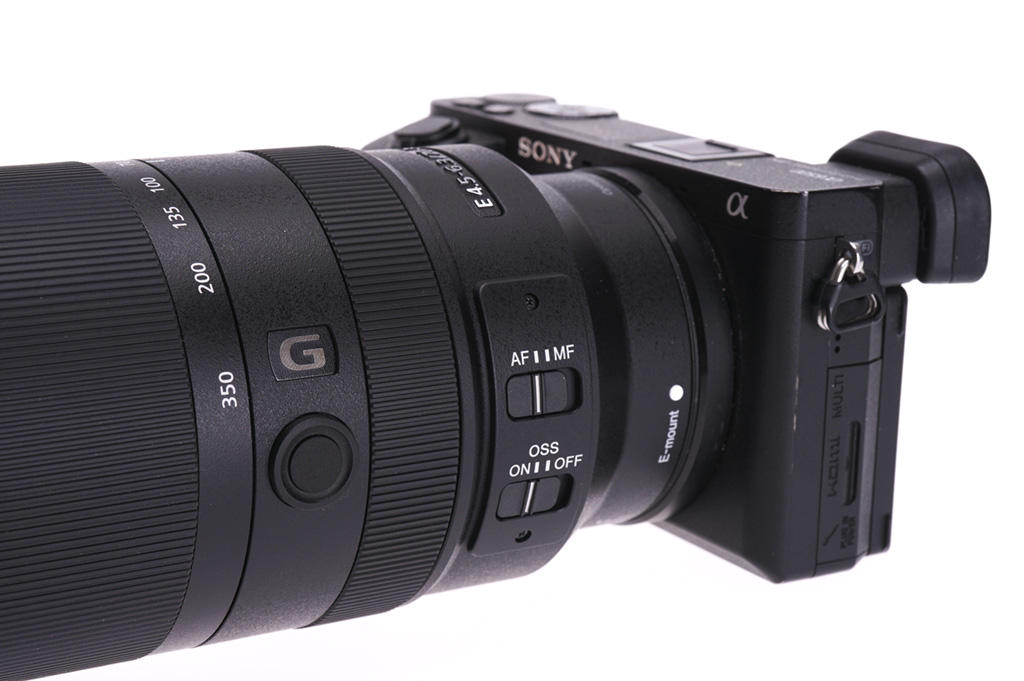

This lens is far better than the 18-200, 18-300, 18-400 or 16-300mm I’ve used on a variety of DSLRs for long APS-C reach. It’s free from the residual aberration which demands you ‘stop down one’ to clean up the long end image. Combined with Sony’s PDAF it handles a concert or low indoor light as well as an ƒ2.8-4 on a conventional DSLR.
Compare this with a 100-400mm for the same format
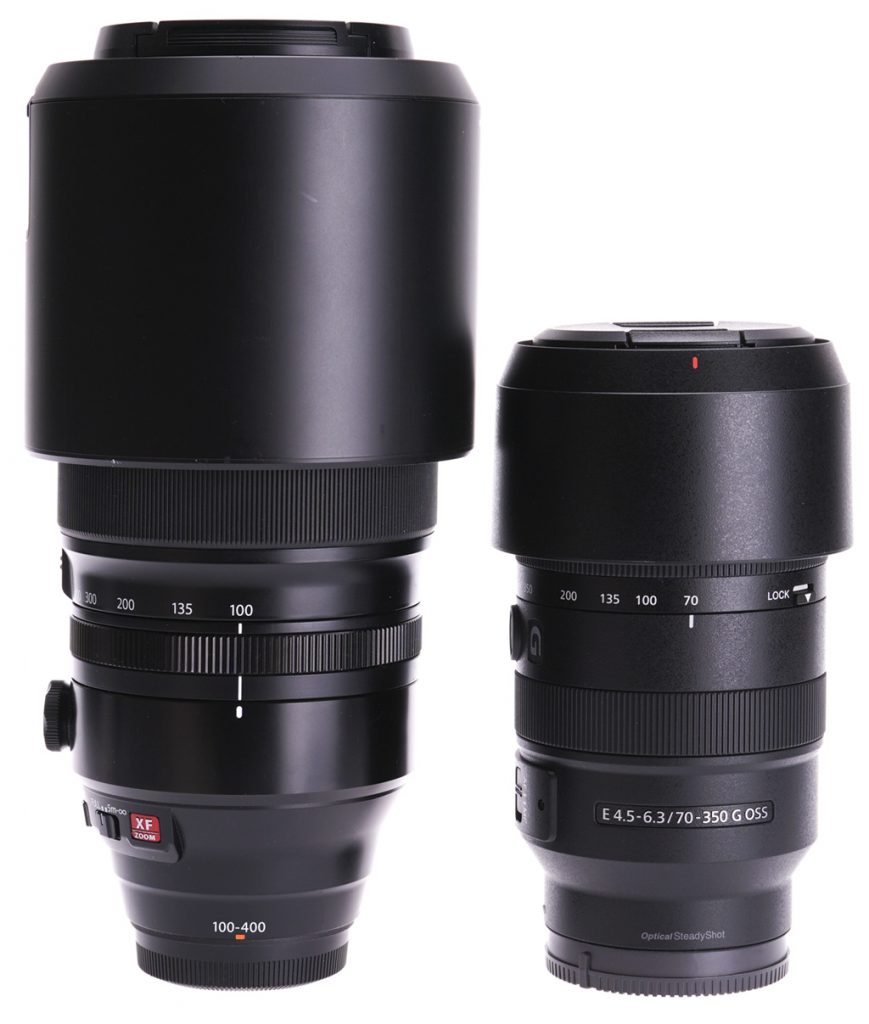

For the sake of 50mm at the long end – a difference of only 12.5% in image scale – the excellent Fujifilm Fujinon XF 100-400mm f/4.5-5.6 R LM also gives a half to a third of a stop more light transmission in its longer range. But look at the cost! It is twice the price and weight, and you can see the size. Gains – a near-apochromatic performance, matched 1.4X and 2X converters available (not an option for the Sony and never likely to be). Losses – only 0.19X close-up scale. It’s remarkable how much difference there is in the physical aspect of these two lenses. I have used both and in practice they are equally sharp on 24 megapixels.
The Sony 100-400mm and Sigma 100-400mm are both full frame lenses and much larger. The 70-350mm is unique as far I can tell, no-one else has a lens like it. It also answers one of the major criticisms of the original E-mount APS-C system, the lack of any lens longer than 210mm and that only in a 55-210mm design best described as consumer grade. I’ve actually found it pretty good for the money – but it’s not much money!
Sony 70-350mm G OSS image gallery
Rather than write much more, I’ll leave you with this gallery. I have reduced the file size but where you see an enlarged section clip along with the full frame – well, you can judge for yourself.
Sony 70-350mm G OSS verdict
If you own any of the APS-C Sony bodies, from the NEX-3 and 5 of 2010 onwards, this lens will not disappoint you. The effective OSS image stabilisation means that even if you prefer to compose and shot using the rear screen and hold the camera away from your body you’ll get sharp stills and steady movies. It’s a big step up from the 55-210mm and much more affordable than, say, a 70-200mm f/4 G with 1.4X or 2X converter.
You may have to control colour fringes in some strong backlight situations with blur when working from raw files, as it’s not an apochromat just a regular very good tele zoom. However the resolution reflects advances in design over the last decade. It’s also a very handsome looking black lens with its silver G logo and designation contrasting with white markings. It feels robust and the zoom and manual focus (when needed) are smooth. The metal bayonet is a tight precise fit on my A6500 and A7RIII, a little less so on my A6000 with its older four-screw type body mount.
I can carry this lens all day without even realising it’s there, round neck or shoulder – and there are not many lenses covering this range you would want to hang on a strap round your neck.
You can support my reviews if you check these links for availability and price:
Amazon UK – didn’t have any stock at all at the time of writing – https://amzn.to/30ZC4Ck
Park Cameras UK – https://tidd.ly/3jLHbP7
WEX UK – https://tidd.ly/3hKRhhA
B&H USA and Worldwide – https://tinyurl.com/y6cguvpo