It’s been a while since my last review of Sony products here, and not because I have been inactive. The truth is that I’ve spent so much on Sony kit 24/7 working has been necessary, including a good few reviews and tests of the A7RII and lenses appearing elsewhere. It’s a real issue, I now lose so much value with the lightning-fast depreciation of Sony’s products within a few months of launch that my old tactic of buying, reviewing and selling no longer works. For one thing, no media in the world will readily pay a fee which even matches the amount you might lose on a camera body in the A7 series over its first two months of retail life. Sony have been good enough to lend me a few items for brief periods but you really can’t form any useful opinions on such radical and new hardware on that basis.
However, my A7R II report is shortly on the way, and the extra time spent using the camera and suffering the damage to my credit card does not harm the process. It helps put the gear in context. I’ve resisted the anti-social pricing policies of the UK camera retail environment for some time, even buying one grey import from Panamoz. So it’s appropriate that my first article for a fair while should be intended to help you save money and get great results from any A7 full frame FE mount camera, while also supporting a company whose UK pricing policies are entirely reasonable – Sigma.

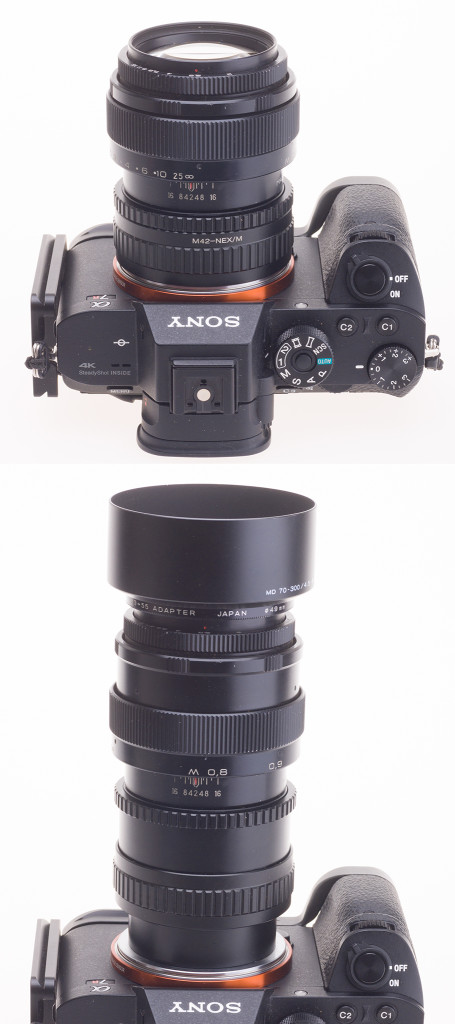
The Sigma 60mm f/2.8 ART DN lens
The butterfly above is one example of what this lens can do on uncropped full frame, in this case adding a single 16mm extension tube, which we’ll come to later as the exact type of tube you buy matters a great deal!

The neat, low-cost 60mm f/2.8 is the portrait lens in Sigma’s Art DN lens trio for APS-C and MicroFourThirds mirrorless systems. I’ve used the 19mm f/2.8 and 30mm f/2.8 as well, but the 60mm is my favourite. Originally, I tested it on Olympus MFT and the 50cm close focus with their 2X factor made it almost feel like a macro. It’s actually just 1:7.2X scale, but 1:3.6X relative to full frame on that smaller sensor. That’s a really good working distance and subject scale.
I was curious to see how much of the full frame the 60mm would cover. All these Sigma lenses are just £129.99-£139.99 retail at most UK dealers right now. They are beautifully designed and made, very light, use 46mm filters and have advanced optical design giving high contrast and first-class full aperture sharpness. Well, the answer is easy enough; you’ll get more than APS-C, with a 24 x 24mm square format crop working well, but not anything like full frame at any aperture from the 60mm.

This is the closest focus of the Sigma ART DN 60mm on the A7R II, uncropped.
Sigma call it a telephoto, with its rear nodal point much closer than 60mm to the focal plane. But its design signalled it would probably perform well as a macro lens too.
Meike extension tubes
So, we add extension tubes between the A7-series body and the lens. There’s one prominent make, Meike, and a couple of years ago I bought their very low-cost fully electronically coupled plastic 10 and 16mm twin tube set. 26mm of extension is not much. It won’t even make the E-mount 35mm f/1.8 focus to 1:1, and does even less with a 60mm. However, what it does is worthwhile combined with the lens’s own focusing range.

I found my plastic Meike tubes have a narrow circular throat and cut the image off all round. But, you say, the image was cut off all round already, so what could be done?
When you mount an APS-C lens on tubes, it covers more than APS-C. Put it on tubes adding about 1.4X to its focal length – like using 26mm of tubes on a 60mm lens – and it will cover full frame. You are moving the lens further from the focused plane, and as you do so, its fixed angle field of sharp coverage grows (it more or less follows the inverse square law, as does the effective working aperture of the lens when you use tubes). So a lens made for the NEX sensors, c.16 x 24mm, can cover 24 x 36mm when used on tubes for close-ups. The 60mm on 26mm of tubes would cover 24 x 36mm even with no leeway. Since the lens already has a good image circle, it turns out that it covers 24 x 36mm when used on the 16mm tube alone, and shows just a hint of corner cutoff with the 10mm tube alone. With both, it covers the full frame easily.


This is the result of using a 10mm metal extension tube – not the plastic set. The plastic design cuts off even more than the lens used on its own.
Meike understand this. They have a newer, metal-mount extension tube set costing about twice as much as the original plastic one. To get it, you must search for Meike metal extension tubes – and they are not easy to identify for certain. There’s very little explanation on-line. These tubes have a full width throat with baffles top and bottom, more or less matching the 24 x 36mm frame shape. Some black flock paper is glued in to prevent light reflection at the sides, but none is fitted top and bottom, and this is the main weakness of the design (you can obtain flock paper and fix this yourself).
Twin set, no pearls

Used alone, the metal Meike tubes turn the Sigma 60mm into a very good close-range long standard lens for the A7 series. I found that you can add the plastic tubes next to the lens, not next to the camera, and suffer no cut-off. This combination of four tubes adds 52mm and makes the Sigma 60mm able to do 1:1 with the addition of its own AF range.

You need to understand sensor-based stabilisation before using any manual lens on tubes (which these are equally suitable for, with adaptors). The A7 II series bodies use the focal length and focus distance of the lens as transmitted to the camera to control the Steady Shot Inside function. As far as I can tell from practical tests, the Meike tubes do not transmit any change to the information reaching the CPU, but SS seems to be OK with such relatively minimal extra focus extension.

This shot was taken at 1/15th hand-held with the 16mm tube on the A7R II, ISO 800, 14-bit uncompressed raw, f/8 on the Sigma 60mm lens. There’s no significant corner vignetting with 16mm of extra extension to the lens.

This is a 100% clip from the shot.
When I mount my 50mm Macro SMC Takumar on the A7R II I use either the SSI menu control, or the Lens Compensation App, to tell the SSI system I’m using a lens with an extension in place. It focuses to 1:2 size, and for this I tell the camera I’m using a 75mm lens not a 50mm. If I add 26mm of tubes, it will focus to 1:1 and I need to tell the camera I’m using a 100mm lens. That’s because a 50mm lens extended to 1:1 focus has the same camera shake characteristics as a 100mm lens used on a distant scene. Be careful, as this relationship only holds good for simple lenses (Tessar, Sonnar etc) and not for any zoom lenses, or any macro lens which uses internal focusing. If you mount a Tamron 60mm f/2 macro on your Sony body using a dumb adaptor, just tell the camera it’s got a 60mm attached. The Tamron changes focal length to focus, but the effect for anti-shake purposes is that it remains a 60mm. Its angle of view remains unchanged as you focus, while my 60mm Sigma when used at 1:1 repro covers half the angle of view it does at infinity.

I am not entirely sure whether the Meike tubes work properly with SS Inside, or if the system simply has enough latitude to function with my degree of unsteady hand-holding. Those contacts just seem to make a connection, with no chip to add information. The EXIF data does show the focal length correctly, and the set aperture (which will be a reduced effective aperture at closer range, 26mm of tubes turns 60mm f/2.8 into a working f/4-ish). But the focus distance is shown as whatever the lens focus function chip confirms – a range of 50cm to infinity. That’s obviously incorrect when tubes are added, in contrast to using a dedicated lens like the Sony 90mm f/2.8 FE G OSS Macro, which will show the true focused distance in the viewfinder and also pass correct data to the CPU.
So, a warning – the 60mm plus tubes is not technically perfect but seems to work well enough.
When you use a tripod or flash, or a fast shutter speed, and turn off Steady Shot none of this applies. In practice with shutter speeds fast enough to stop subject action or wind vibration, it all goes well. The Sigma is very sharp even though not designed for macro range work, but that’s typical of this type of lens – even if 8 elements in 6 groups with several low-dispersion elements is not basic.
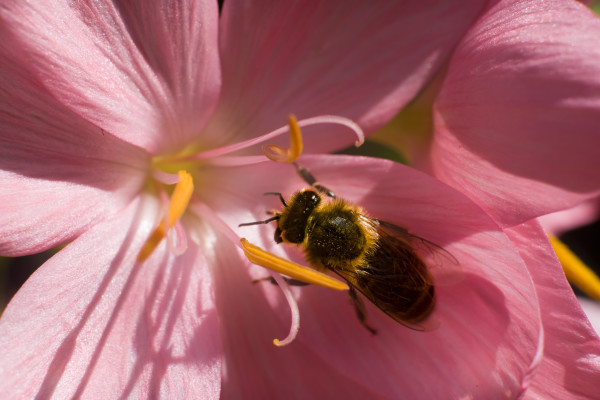

Here’s an example with 26mm of tubes plus some lens focus range. The ISO 800 14-bit uncompressed file has allowed some work on the bee’s back which lacked contrast. Click to open a 2048 pixel wide version.
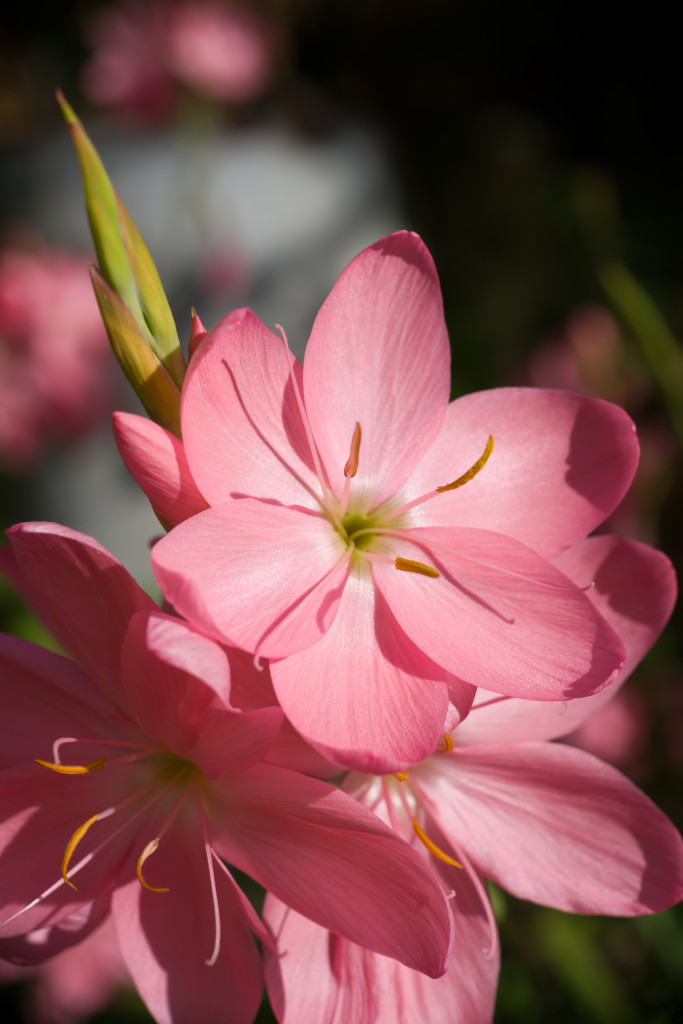

Here’s an example which clicks through to a full size A7R II AdobeRGB JPEG (no doubt much crunched by WordPress image storage) taken at f/9 on the 16mm tube. If any of my image files have 20mm in the filename it was the 16mm tube – I’m so used to the lengths used by regular SLR mounts! The 60mm has a seven-blade aperture and gives pleasantly neutral defocused quality behind the subject. You can call it bokeh if you want to. Thank you, Scottish weather, for keeping a few flowers in this condition and giving me some sunshine just after the 14-bit uncompressed raw upgrade for the A7R II arrived.
The Metal Meike extension tubes have the same essential benefit over the plastic version with all FE and E mount, and legacy, lenses used of the A7 series full frame bodies. You can use them on the 28-70mm, 24-70mm, 55mm f/1.8, 28mm f/2 and most lenses though they have little use with the 70-200mm and I would not recommend hanging a 24-240mm off a tube.
Footnote July 2017: I now have the 50mm f/2.8 FE Sony macro. It’s a very nice lens, indeed, but the internal focusing means it’s really more like a 40 to 35mm as you get the subject bigger, and you end up just millimetres away. I compared using this lens on 26mm of tubes to focus on a target 7.5cm wide with the lens itself set to infinity (and therefore, 50mm). Working distance from the lens rim to subject – 11cm. Then I took the tubes out, and focused the lens using its own range, on the same target. The clear distance was reduced to 7.5cm. Now you know why you need tubes and probably don’t really need a macro lens.
– David Kilpatrick
If you have found this article useful, you can support Photoclubalpha by using affiliate buying links (we are not sponsored or paid in any other way, except by selling subscriptions to f2 Cameracraft).
Sigma 60mm at B&H
Vello metal mount extension tubes at B&H (similar to Meike)
Sigma 60mm F2.8 DN for Sony E – Silver from Amazon UK, no idea why they have none in black
from Amazon UK, no idea why they have none in black
Neewer metal extension tubes – much better price than Vello! on Amazon
Visit Wex Photographic and search for any items (UK)