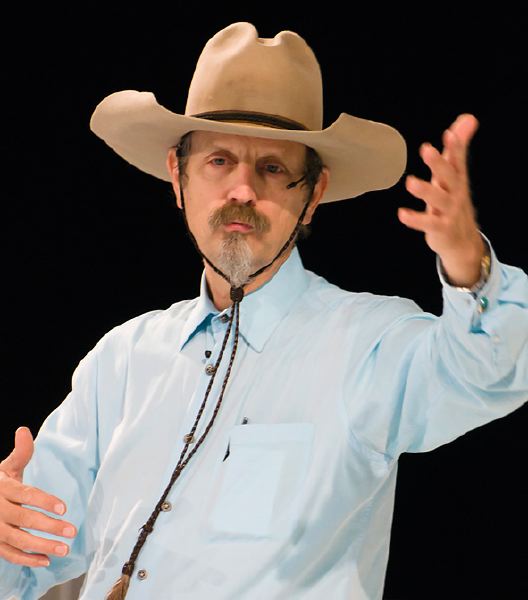
We shall be sending Frank Doorhof one of our original and rare Alpha Male T-shirts, in black, though I’m not sure we have anything quite large enough to fit him – which goes for his personality too. He’s a great workshop presenter, overcoming technical problems by just cracking on with whatever will work best. At Edinburgh for The Flash Centre’s full day fashion seminar with Frank on May 24th, the last thing I expected was to be using the same camera as Frank. All workshop leaders use Canon, right?
Frank now uses Sony Alpha 99, and he had a lot to say about it. Since we already know the benefits of the Alpha system and the current Sony full frame 24MP sensor with its extreme 14-bit dynamic range, most of what he said was not new, but it’s rare to hear a course leader extol the virtues of a system which not one of his delegates (apart from me) was using. He did rather talk down the value of CZ lenses (while using a 24-70mm CZ) and praised the quality of his vintage Minolta 85mm f/1.4 and 35-200mm xi, but I can’t argue with that as I’ve made similar decisions. Indeed, the 35-200mm owes much of its reputation to results we published seven years ago. I was beating him at his own game by using my SAM 28-75mm f/2.8 – cheaper by half than the CZ 24-70mm, and extremely sharp.
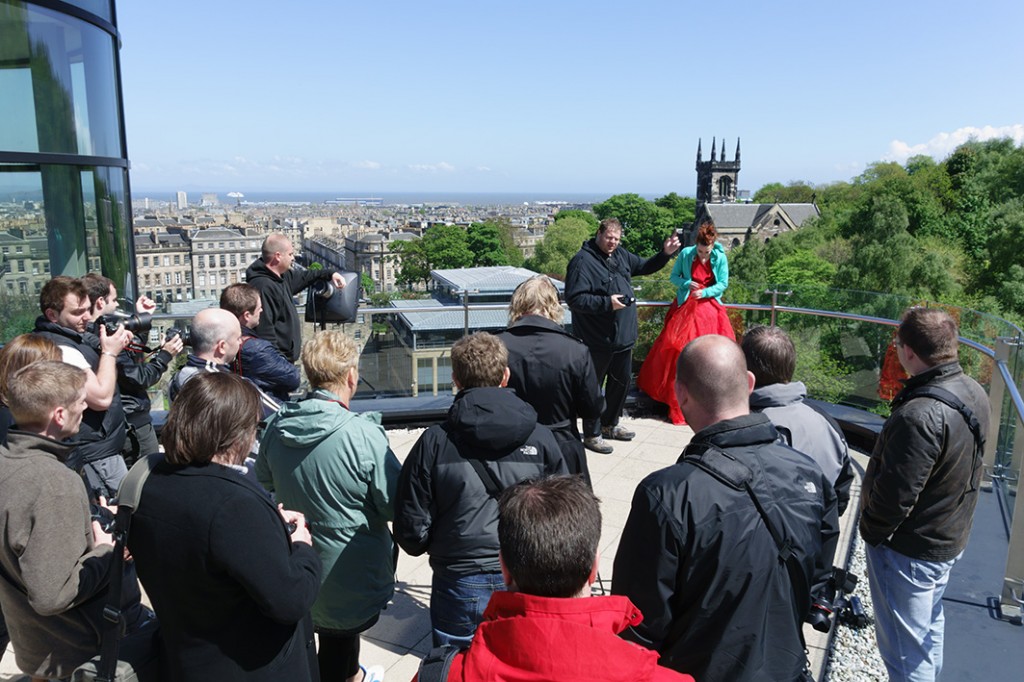

We had a rare sunny clear day in a run of mixed weather, though it was cold and windy on the roof terrace of the Glasshouse Hotel in central Edinburgh. The location provided strong backgrounds and details. Simon Burfoot and Chris Whittle from The Flash Centre brought along the Ranger (battery location) and Ranger Quadra (lightweight version) flash systems with Elinchrom Skyport wireless triggers. Of course, in the past if you turned up to a workshop with an Alpha body, you were unable to use the wireless flash connection unless you also remembered to bring a standard hotshoe adaptor. With the A99 (and NEX-6, RX1 and future models) the new Alpha multi function accessory shoe works directly with triggers.
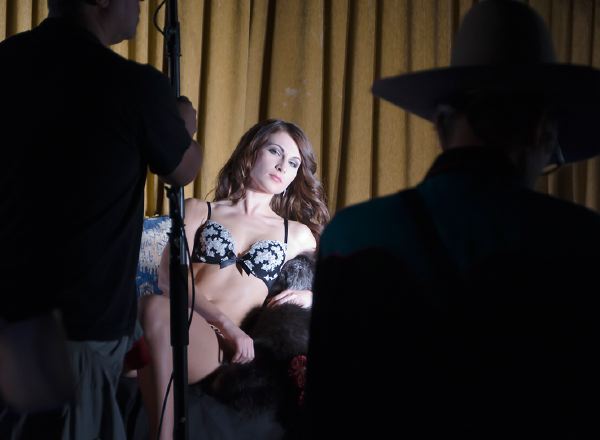
Frank put everything into using just one light source, and used no reflectors, aiming instead for dramatic lighting by underexposing the main scene but lifting his model subject Nadine by local flash. This was achieved with the 44cm rigid square softbox, newly re-introduced to the Elinchrom system (I have used the original grey one for over 20 years – you only need to buy these expensive accessories once in a lifetime). Fitted with a honeycomb but no diffusing scrim, the single lighting head with this light shaper put a tightly controlled pool of light on to his subject. Though it’s easy to use digital SLRs as a pre-test light metering and flash balancing method, Frank works with a Sekonic flash and ambient light meter able to take incident, reflected and partial spot readings. It is very similar to the discontinued classic Minolta Flashmeter IV/V, with the same 1/10th stop accuracy and display of contrast and memorised values. If I was doing this type of work, I would use my Flashmeter IV, but I would also use its calibration function to match it to specific ISO settings on the A99.
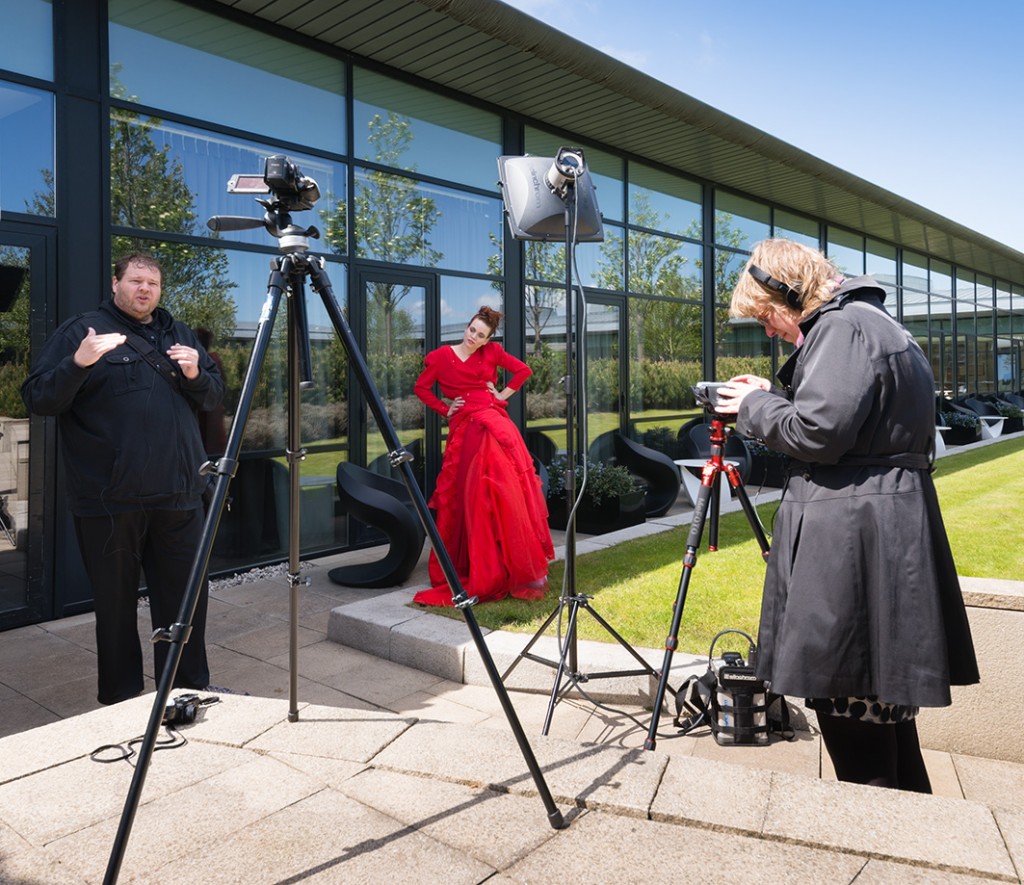

Frank’s wife Annewiek used multiple video cameras to film the workshop, as Frank provides his on-line tutorial material through Scott Kelby’s training site. Here you can see one set-up as he explains how he’s seeing the location, addressing the used of the glass window wall, avoiding unwanted reflections, placing Nadine in the shade then adding the flash to match an underexposed daylight scene. To achieve the required settings, he used ISO 100 at apertures around f/16 to f/22, with a 1/160th shutter speed, and mechanical first curtain shutter. I also followed these settings, which are not kind to sensor dust spots. Anyone using a Nikon D600 would have been in serious trouble! Even my ‘clean’ A99 which never needs any spot removal at my regular optimum working apertures between f/8 and f/13 showed a few visible spots at f/18. I would have used ISO 50, which I consider to be an advantage of the A99, and trusted shutter speeds to 1/250th with this camera for flash sync. But Frank was dealing with photographers some of whom had cameras incapable of shooting at less than ISO 200 or synchronising with studio flash at 1/250th without a slight second curtain crop to the frame. It would not have been fair to demonstrate using the advantages of the Alpha 99…
I did have in my bag, and normally carry, a 4X ND filter. With the Alpha 99, fitting an ND filter has absolutely zero effect on the viewfinder brightness, or the quality of view in sunlight. After all, sunshine with a 4X ND is just like a cloudy day in brightness, and you have no problems on a cloudy day. You can work with an ND just as ‘transparently’ as you can use an UV filter. An alternative would have been to use a polarising filter, which can also enhance the dramatic ‘dark sky – bright subject’ mix. However, Frank wisely kept clear of this. Polarisers have some pretty horrible effects on fabrics, skin and hair. Use them on portrait or fashion shots only with great care. Digital sensors are usually able to do deep blue skies without help.

Here’s the Elinchrom Ranger head as used. Frank asked delegates to restrict themselves to three shots per situation, a request generally ignored. I took some before the flash had recycled, to show the effect of the scene without flash, and with flash.

This was my ‘take’ on this setup and it’s probably different from most as I used a 12-24mm Sigma HSM lens at 12mm. Now Frank did not explain to the photographers how he was using his electronic viewfinder, and I didn’t ask, but I’m sure he had it set to over-ride manual setting gain, as he was shooting on manual (M) with a degree of underexposure that would have made the finder extremely dark. I didn’t change my setting and though for all the other situations I was able to compose well enough, for this set-up my EVF showed nothing but solid black where the model was. As a result, I did not see what an ungainly shape was made by the extreme angle of the 12mm lens for a couple of poses.

The left hand side is very much how my finder looked. I don’t like this result, but I could not tell until after it was taken. Nadine was changing poses rapidly. This is one case where the optical viewfinder of my Alpha 900 would have been a better choice.
If you have a Sony/Minolta wireless flash set-up, you can overcome this whole problem. Your remote flash would perhaps need a softbox, or more realistically a small umbrella to match Frank’s localised soft flash and also receive the control signal from the on-camera flash. You would simply set the remote flash to Manual power not TTL, set the A99 (or other EVF DSLR) to Aperture Priority (A), set f/20, and rely on the flash’s auto communication with the camera body to set 1/160th flash sync and ignore the ambient light. You can also do the same with a slave cell triggered by a small camera top unit converted to invisible IR using a gel filter or old transparency unexposed film-end. You can not do this with the sync cable (PC socket) or flash triggers, as these connections do not tell the camera there is a charged flash fitted, and set the shutter speed.
Elinchrom! We need, for Sony and other EVF or LCD screen-only cameras, a flash trigger designed to provide a signal to the pin which the camera’s own flash system uses to auto-set flash sync speed when using Aperture priority. When this is live, the viewfinder brightness is set to auto gain regardless of the exposure mode (PASM) used.
For his first set-up, Frank was actually shooting full lengths from a distance with Nadine making a small element in a large view. I liked the structure she was posing under, and prefer in general to get pictures which are not a copy of the course leader’s work. Although this was also slightly underexposed for the background, I had no problem with the EVF when the subject was in a normally lit area.

You may say, the subject was in sunlight anyway, so why use flash? The dual lighting gives a filmic look, like a movie set lit in Californian sunshine (and Scotland’s legendary blue skies complete the illusion). This essentially sidelight from the sun, with a frontal fill you can see most clearly on the fingers of the left hand glove.
For a further set-up, Frank moved to the roof terrace view over the north of Edinburgh towards Leith and the Forth (first image on this page). He had demonstrated sets suitable for normal to wide angle lenses, using the 24-70mm, and switched to the 70-200mm f/2.8 Sony SSM G for a different relationship between the model and the background.

This was the view without flash – not a bad set-up as it stands. When processing my images, I found that the in-camera standard JPEGs of the A99 handled the red of the dress better than almost any setting or camera profile using Adobe Camera Raw. Colours like this are a good case for trying alternative raw converters, such as DxO Optics Pro or Capture One Pro. Their camera profiles are generally closer to the in-camera conversions than Adobe’s. Frank demonstrated how to use the MacBeth ColorChecker Passport colour patch target and its camera profiling software to create an on-the-spot profile for better ACR/LR conversions.

This is the shot with flash, again, in-camera JPEG sRGB. AdobeRGB would retain more potential detail in the red, raw conversion to 16-bit using ProPhotoRGB the maximum. But for that you also need something like a Eizo 10-bit monitor with a matching video driver, and no Apple Mac made comes with that. Build yourself a tower system and it’s just about possible to get 10-bit colour… but not using Mac OSX! My monitor is a regular old 27 inch iMac and if it’s 8-bit it’s having a good day. The colour looks lovely, but accurate it certainly is not. I don’t mind as 99% of all the screens any of my images will ever be seen on are no better, and the printed page is far inferior. Putting the above pictures into print would almost guarantee the differences you see here are lost.

Because the Glasshouse’s rooftop function suite has a white translucent fabric roof, the overhead projector could not be used. So, Frank sat down with his laptop and the photographers. Later on in the day, the group moved to an inside room, and he demonstrated a series of processing steps in Lightroom with special attention to the use of plugins producing Clarity, pseudo-HDR and ‘image look’ and to fashion and beauty retouching.
To read more about Frank’s work, visit his own website www.frankdoorhof.com or follow him via Kelby Training. He regularly does workshop tours. I’ll be reporting on some of his views and hints for professional photographers, specifically, in the June 2013 edition of Master Photography magazine (you can subscribe here for this 10X a year magazine which we also produce).
For more information on the Elinchrom flash system, Skyport wireless triggering and battery powered Ranger/Ranger Quadra location flash, see The Flash Centre website.
– David Kilpatrick